Case Study: How Jio's Cut-Throat Strategy Disrupted the Indian Telecom Market
Introduction
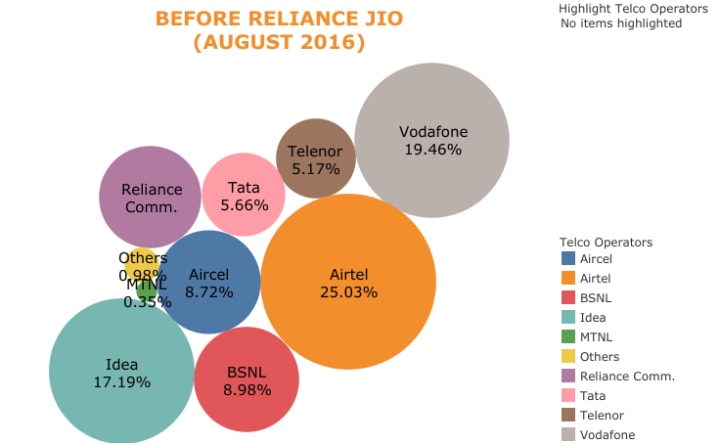
In 2016, Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited, a subsidiary of Reliance Industries, entered the Jio telecom market disruption India with a strategy that would transform the industry forever. By offering free voice calls and drastically reducing the cost of data services, Jio implemented a classic cut-throat strategy. This move not only led to Jio’s rapid dominance in the market but also forced many existing telecom operators, including Aircel, Tata Docomo, and Idea, to either exit the market or merge to survive.
The Launch and Initial Strategy
- Date: September 5, 2016
- Initial Offer: Jio launched its services with a three-month introductory offer, providing free 4G data, voice calls, SMS, and access to a suite of Jio apps.
- Impact: This aggressive pricing led to a massive customer acquisition, with Jio gaining 50 million subscribers within just 83 days.
Disruption in Pricing
Jio’s entry led to a significant reduction in data prices across the industry:
- Pre-Jio Data Cost: Before Jio’s entry, 1GB of 3G data cost around INR 250-300.
- Post-Jio Launch: Jio offered 1GB of 4G data at an average cost of INR 50, reducing the price by 80-90%.
- Voice Calls: Jio’s free voice calls forced other operators to offer unlimited calling plans at reduced rates.
The Collapse of Competitors
Jio’s cut-throat strategy led to severe financial stress for other telecom operators:
- Aircel: Filed for bankruptcy in 2018 due to mounting losses and inability to compete.
- Tata Docomo: Exited the market by merging with Bharti Airtel in 2017 after suffering heavy losses.
- Idea and Vodafone: Merged in 2018 to form Vodafone Idea Limited (Vi) to survive Jio’s competition. Despite the merger, Vi struggled with debt and declining market share.
Evolution of Jio’s Pricing Strategy
After establishing a strong foothold, Jio gradually transitioned from its free and ultra-low-cost services to more sustainable pricing:
- 2017: Launched various prepaid plans, starting at INR 149 for 1GB data per day and unlimited voice calls.
- 2019: Introduced JioFiber, expanding into broadband services with competitive pricing.
Long-Term Impact on the Industry
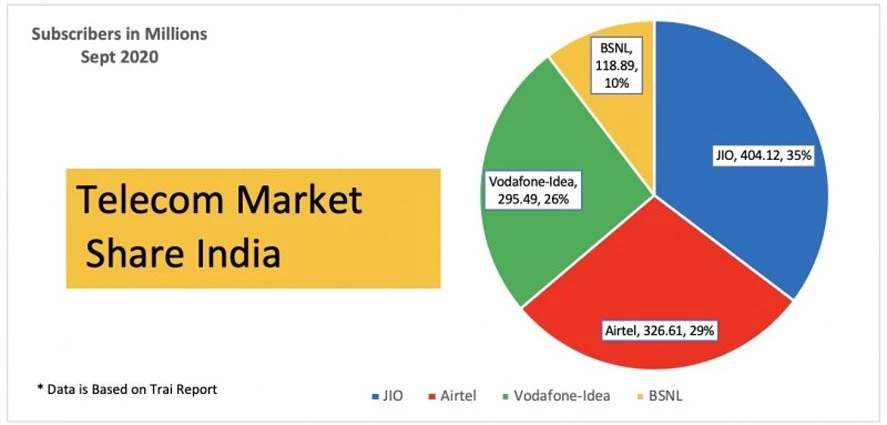
- Market Share: By 2021, Jio had captured over 35% of the market share, becoming the largest telecom operator in India.
- Industry Consolidation: Jio’s entry led to the consolidation of the industry, with only three major players (Jio, Airtel, and Vi) remaining.
- Digital Revolution: Jio’s affordable data plans fueled a digital revolution in India, leading to a surge in internet users, digital payments, and online content consumption.
Competitive Edge Through Infrastructure Investment
One of the lesser-discussed aspects of Jio telecom market disruption India is Reliance Jio’s substantial investment in next-generation infrastructure before launch. Unlike legacy players that relied on existing 2G and 3G networks, Jio built an all-IP 4G LTE network from the ground up. This allowed the company to deliver superior data speeds and network reliability at scale. Backed by deep financial reserves from Reliance Industries, Jio installed over 250,000 cell towers and laid out an extensive fiber-optic network across the country. This infrastructure-first approach ensured that the telecom operator could offer unmatched services without the quality issues plaguing competitors. It not only provided Jio with an operational edge but also helped gain consumer trust rapidly.
Jio’s entry was not just about low pricing—it was a comprehensive ecosystem strategy. Alongside free data and calls, users were given access to a wide range of proprietary apps like JioTV, JioCinema, JioSaavn, and JioNews. These digital offerings increased customer stickiness and further deepened the Jio telecom market disruption India. Competitors struggled to match this holistic model, as most lacked the integrated tech ecosystem or capital to do so.
Transformation of Consumer Behavior
The Jio telecom market disruption India did more than disrupt corporate balance sheets; it transformed how Indian consumers interacted with mobile technology. Before Jio, data usage was largely limited due to high costs. Post-launch, India became one of the largest consumers of mobile data globally. Video streaming, social media engagement, and mobile app usage surged as data became more accessible and affordable. This shift prompted a domino effect across industries—startups boomed, e-commerce adoption increased, and online education platforms gained massive traction.
Jio’s move also catalyzed the adoption of digital payment systems. UPI (Unified Payments Interface) transactions saw exponential growth, and mobile wallets became mainstream. In rural areas, access to information, education, and entertainment reached unprecedented levels. The impact of the Jio telecom market disruption India went beyond economics; it was a social and digital awakening that redefined how India communicates, learns, and does business.
In conclusion, Jio’s strategy was not merely cut-throat—it was visionary. By reshaping pricing, infrastructure, and consumer habits, Reliance Jio redefined the Indian telecom landscape. The Jio telecom market disruption India serves as a textbook case of how aggressive innovation can dismantle old structures and build new digital ecosystems.
Conclusion
Reliance Jio telecom market disruption India cut-throat strategy not only disrupted the Indian telecom market but also redefined it. By offering free voice calls and drastically reducing data prices, Jio forced competitors to either adapt, merge, or exit. This case study exemplifies how aggressive pricing and innovative strategy can lead to market dominance and long-term industry transformation.
